18.11.2024
Digital Accessibility in the agile UX process
What are the requirements of the Barrierefreiheitsstärkungsgesetz (BFSGV)? How does accessibility influence the UX design and the development process of digital products? What approaches are there to effectively design accessible digital services? In this article, we summarize what you should pay particular attention to when implementing accessible design and give you tips for successful integration into the product development process.
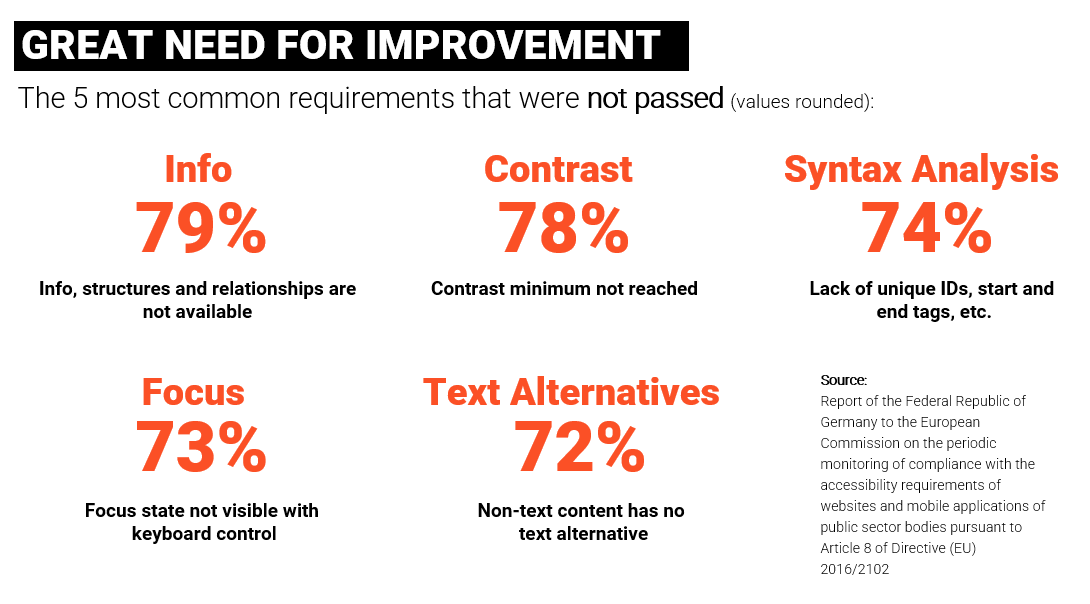
There is still a lot to do when it comes to digital accessibility. This is shown, for example, by the BFIT-Bund monitoring report, which tested over 1000 websites according to 50 success criteria. The results show that there is a great need for improvement in the area of accessibility. Below we show you an overview of the 5 most common requirements that were not met:
Added value through accessible design
In summary, it can be said that the target group of people affected is much larger than often assumed, as it includes not only people with disabilities, but also older people or people with temporary disabilities. The expansion to new perspectives creates new opportunities for innovation and improvement. Products also benefit from the curb-cut effect: accessibility measures often also benefit people without disabilities by making everyday life easier for everyone. In addition, barrier-free design enables you to meet legal requirements – see next section.
Regulations on digital accessibility
Accessibility Reinforcement Act
The Accessibility Reinforcement Act (BFSG) implements the EU Accessibility Directive (European Accessibility Act) in Germany. The law will come into force on June 28, 2025. It expands the existing regulations to include the entire digital sector and defines new standards to make products and services accessible. In addition, the scope of the law will be extended from the public to the private sector.
WCAG 2.1.
WCAG 2.1 plays an important role for us designers. These guidelines were developed by the Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI) of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and set the international standard for the accessible design of online content in the EU. The WCAG 2.1 guidelines are a helpful guide for all stakeholders who want to and have to implement the Accessibility Improvement Act in the future.
Which areas are subject to accessibility requirements?
Public bodies
The accessibility requirements increasingly affect the public sector. These institutions include public authorities, hospitals, courts and local authorities, as well as universities and savings banks. The accessibility requirements for public bodies cover the following areas, among others:
- Websites (Internet & Intranet)
- Mobile apps
- Electronic processes and documents in administration
- Graphical user interfaces
- …
B2C
In the B2C sector, the requirements of the BFSG apply to companies that generate a turnover of more than 2 million euros or employ more than 10 people. In this sector, the following services and products are affected by the requirements:
- Computers, tablets, smartphones and operating systems
- Telephones and other telecommunications equipment
- Self-service terminals
- Devices for audiovisual media services
- Audiovisual media services: music / films
- E-book reader, e-books / software for reading
- E-Commerce / Online stores
- Passenger transport services: Websites, apps, electronic tickets, information kiosks, self-service terminals
- Online courses
- …
Context-sensitive accessibility in B2B
If a product or service is used in specific B2B contexts, the aim of development is not to implement accessibility guidelines 1:1 so that everyone can use the application with their individual limitations. The focus is on providing specialist personnel with efficient access. In the industrial environment, with complex B2B applications or medical software, we speak of context-sensitive accessibility. Considering potential barriers is also important in this environment, as these applications are used in complex and demanding environments.
One example is industrial applications, where touch terminals are often used without a keyboard or audio input. Operation must also work in difficult lighting conditions and with thick gloves. Noisy production halls also require visual alarms or clear graphic instructions instead of audio signals to warn of errors.
A11Y – Implementing digital applications without barriers
In the agile development process, accessibility should not be seen as an afterthought, but as an integral part of every phase – from project initialization to delivery.
Project initialization
The first step to successfully incorporating accessibility into a project is to raise awareness throughout the entire team and to empower all employees accordingly. You should ensure that accessibility is integrated into the various project levels as early as the project initiation phase:
- Planning for accessibility right from the start means that you consider and plan for accessibility and extended target groups as early as the target and product definition stage.
- Ensure that you have sufficient specialist resources who are familiar with accessibility and thus enable product owners to define the product requirements accordingly
- Design and development should be trained according to the BITV specifications so that they are familiar with the accessibility requirements and can integrate and check them.
- You should also expand your quality assurance to check accessibility in the individual development steps.
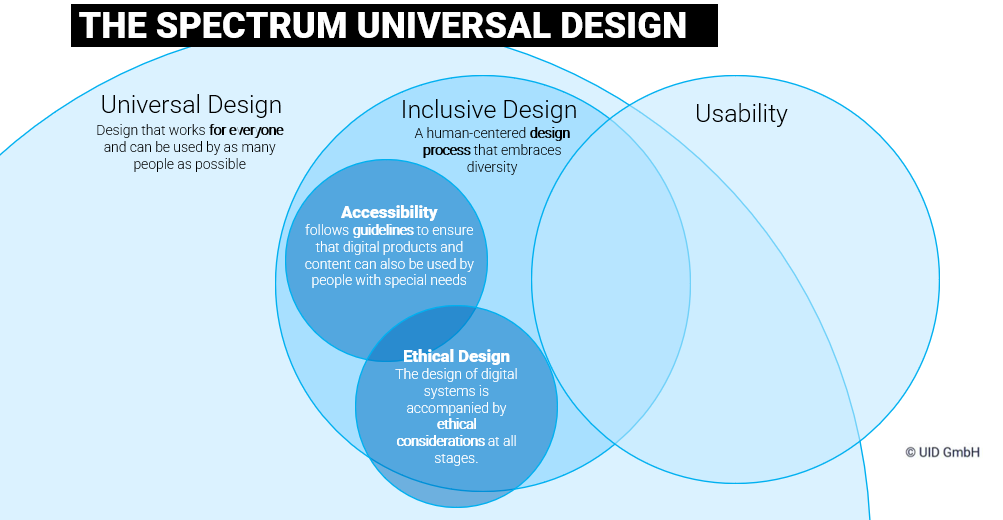
EXCURSE: Inclusive Design – How to think inclusive from the start
For our projects, we have developed an approach that creates awareness for inclusive design and trains your project team to think inclusively.
Because in product development, we often focus on the ideal user, the so-called “happy path”. But what happens to our product if we don’t think inclusively? And how can we make the transition from a “happy path” to an “inclusive path”? In a joint workshop, we will first work out the requirements of people with different limitations for your product. We then analyze the implications of integrating these inclusive features and the potential challenges and risks that may arise.
This is how we create awareness for inclusive design and accessibility and demonstrate ways of thinking outside the box.
UX Research
- Clarify the requirements for your research measures: Where will the product be used? What legal requirements apply? Do we understand the needs of the users?
- Expand the user groups by defining diverse user groups and involving them in the development process.
- Creates personas for target groups with disabilities.
- Integrate testing into your development steps: Continuous testing throughout the development process is essential, whereby we recommend a balance of 30 % automated and 70 % manual tests.
- Manual testing is suitable for finding out whether your application is accessible. This is where experienced and certified testers who are familiar with WCAG/BTIV come in and check your product for accessibility. Public bodies in particular must provide evidence of such a check in a test report.
- In Automated Tests, you can quickly and easily check your applications in advance and during the process using tools such as AXE, WAVE or Lighthouse.
- User tests are particularly important to cover accessibility, as you can integrate real users with various limitations into the development process and have the product evaluated from the perspective of the various limitations/disabilities. We have cooperations with associations that provide such target groups with the corresponding profiles. This allows you to identify pain points and needs of different impairments and at the same time identify special features in the context of use (e.g. lighting conditions) to identify further barriers.
UX ideation, concept & design
- Expand your concept to include the defined accessibility requirements.
- Performs manual tests with designed screens.
- Adapt your prototype development to test scenarios and extended user groups.
- Regularly obtains feedback from user tests.
Implementation
- When handing over to development, it is important to anchor accessibility in design tools such as Figma. It is best to create a list of requirements that sets out the properties for the various elements.
- This documentation enables developers to take accessibility requirements into account and ensure that all components comply with the specified standards.
- Integrates A11Y testing even after implementation for further releases.
Accessibility check

By the way: Accessibility requirements are always covered in our projects. This is because we use our own checklist to ensure the accessibility of your application. We have translated the WCAG requirements into a checklist and work along the criteria with various areas and test sections. You and your product will benefit from this structured accompanying document in our projects!
Conclusion
In order to create a positive awareness of accessibility (A11Y), it is crucial that the entire team is involved in the process from the very beginning. All areas, including project management, UX design and development, should take responsibility for A11Y. Continuous testing in the development process is essential, especially with diverse user groups. This is where collaboration with organizations and associations for people with disabilities helps to incorporate their perspectives and needs directly into the development process. And very important: after testing is before testing! Integrate A11Y testing even after the release.

As Creative Director and UX Lead, Stefanie Angele is responsible for the holistic UX development of digital products at UID GmbH. Together with the innovation team at UID in Munich, Stefanie works closely with users and customers to develop requirements, designs interaction concepts with testable prototypes and creates innovative products for the world of today and tomorrow. In her position as UX strategist, she also develops future scenarios, taking into account new technologies and trends, in order to base corporate strategies on well-founded assessments that have taken on new significance in the context of digital transformation.
Sources
- https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/accessibility
- https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/inclusive-design
- https://inclusive.microsoft.design
- https://www.bmas.de/DE/Service/Gesetze-und-Gesetzesvorhaben/barrierefreiheitsstaerkungsgesetz.html
- https://www.barrierefreiheit-dienstekonsolidierung.bund.de/Webs/PB/DE/gesetze-und-richtlinien/wcag/wcag-artikel.html
- https://www.lf-barrierefreiheit-st.de/digitales/webseiten/normen-und-richtlinien
